Help Prevent Further Trauma with Differential Diagnosis of Dizziness or Vertigo
Today we get to hear from Mitch Owens, MsPT, COMT who is the author and instructor of "Neck Pain, Headaches, Dizziness, and Vertigo: Integrating Vestibular and Orthopedic Treatment". Join Mitch in Rockville, MD on November 14-15 in order to learn more about treating patients with head trauma.
 Following a whiplash injury, concussion or vestibulopathy patients will complain of the same cluster of symptoms: neck pain, dizziness, and headache. In order to properly treat patients complaining of these symptoms a clinician must first be able to determine the source and understand the physiology at work to reason out the best plan of care.
Following a whiplash injury, concussion or vestibulopathy patients will complain of the same cluster of symptoms: neck pain, dizziness, and headache. In order to properly treat patients complaining of these symptoms a clinician must first be able to determine the source and understand the physiology at work to reason out the best plan of care.
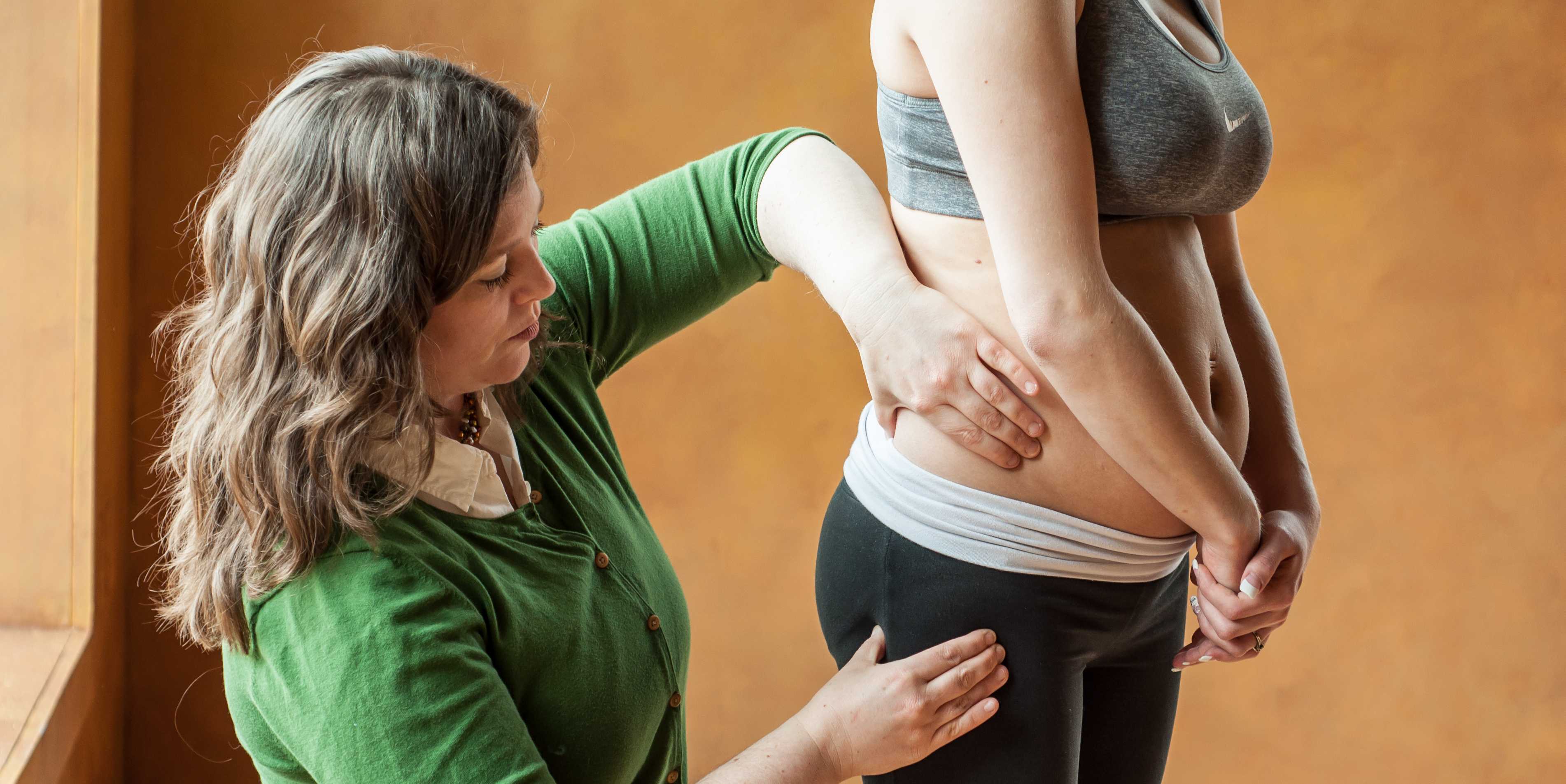
Treating individuals for dizziness, neck pain and headaches requires a refined understanding of the systems involved, the clinical tests that can be used to differentiate symptom generation and then finally which evidence based interventions should be deployed.
A patient who presents with a complaint of dizziness or vertigo following a trauma to the head or neck will challenge the examination skills of even the best practitioners. The list of differential diagnosis includes a number of conditions that could prove to be quite threatening to the patient with or without intervention. These conditions include: vertebral basilar insufficiency, cervical fracture, dislocation or instability, stroke, traumatic brain injury, concussion, and peripheral vestibulopathy to name a few. The ability to clinically reason and properly assess these individuals is crucial to the effective management of any orthopedic or neurologic case load.
Clinicians treating either population need skill sets that bridge the orthopedic and neurologic expertise gap that often exist if clinicians. The need to close this gap is highlighted the following facts:
- 15-20% of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo is caused by trauma (Gordon, Carlos et al. 2004).
- 19% of cases of whiplash demonstrated vestibulopathy with videonystagmography (VNG) testing within 15 days of their accident (Nacci, A. et al 2011).
- 60% of cases of whiplash with head trauma demonstrated vestibulopathy (Nacci, A. et al. 2011).
- Dizziness is reported 20-58% of whiplash patients (Wrisley DM et al. 2000).
- Between 40%-70% of individuals with persistent whiplash associated disorders complain of dizziness (Treleaven, Julia et al. 2003).
- The incidence of cervicogenic dizziness has been reported to be 7.5% of all dizziness (Ardic FN, et al. 2006)
Recent evidence has shown that sensory dysfunction is as much a part of dizziness as it is a component of chronic neck pain (Treleaven, Julia et al. 2003).
Interventions directed at training cervical proprioception have been show to significantly reduce pain and has improved function in patients with chronic neck pain (Revel, Michel, et al 1994). Manual therapy techniques directed at the upper cervical spine have also been shown to effectively treat dizziness in randomized control trials (Reid, Susan A., et al. 2013).
Thus we are learning the ability to effectively measure and treat neurologic dysfunction is an important part of address cervical spine issues. It is equally true that being able to assess and treat cervical spine dysfunction is an important part of treating patients who complain of dizziness.
Enhancing your neurologic and orthopedic skill set is clearly useful for any clinician and will help improve your outcomes across all patient populations. Continued training in these areas will expand what patients you can see, add to your clinical tool belt, and improve your confidence within your current caseload.
References:
Ardic FN, Topuz B, Kara CO. Impact of multiple etiology on dizziness handicap. Otol Neurotol. 2006;27:676 – 680.
Gordon, Carlos R., et al. "Is posttraumatic benign paroxysmal positional vertigo different from the idiopathic form?." Archives of Neurology 61.10 (2004): 1590-1593.
Nacci, A., et al. "Vestibular and stabilometric findings in whiplash injury and minor head trauma." Acta Otorhinolaryngologica Italica 31.6 (2011): 378.
Reid, Susan A., et al. "Comparison of Mulligan Sustained Natural Apophyseal Glides and Maitland Mobilizations for Treatment of Cervicogenic Dizziness: A Randomized Controlled Trial." Physical therapy (2013).
Revel, Michel, et al. "Changes in cervicocephalic kinesthesia after a proprioceptive rehabilitation program in patients with neck pain: a randomized controlled study." Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation 75.8 (1994): 895-899.
Treleaven, Julia, Gwendolen Jull, and Michele Sterling. "Dizziness and unsteadiness following whiplash injury: characteristic features and relationship with cervical joint position error." Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 35.1 (2003): 36-43.
Wrisley DM, Sparto PJ, Whitney SL, Furman JM: Cervicogenic dizziness: a review of diagnosis and treatment. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy 2000, 30(12):755-766.
By accepting you will be accessing a service provided by a third-party external to https://www.hermanwallace.com/