The following is part three in a series documenting Deb Gulbrandson, PT, DPT's journey treating a 72 year old patient who has been living with multiple sclerosis (MS) since age 18. Catch up with Part One and Part Two of the patient case study on the Pelvic Rehab Report. Dr. Gulbrandson is a certified Osteoporosis Exercise Specialist and instructor of the Meeks Method, and she helps teach The Meeks Method for Osteoporosis course.
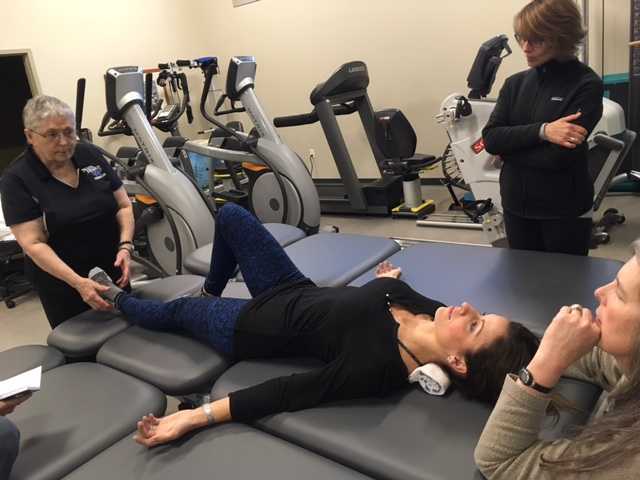 On Maryanne’s third visit, after reviewing her home exercises I told her that today our focus was on alignment. “In dealing with osteoporosis we want the forces that act upon our bodies to line up as optimally as possible. We have gravity providing a downward force from above and we have ground reaction forces coming up from below. Remember back to your first visit when we did the Foot Press in sitting and talked about Newton’s 3rd Law? For every action there’s an opposite and equal reaction and, how by pressing your feet down it helped you to sit straighter and gave more support to your back?” She nodded in agreement.
On Maryanne’s third visit, after reviewing her home exercises I told her that today our focus was on alignment. “In dealing with osteoporosis we want the forces that act upon our bodies to line up as optimally as possible. We have gravity providing a downward force from above and we have ground reaction forces coming up from below. Remember back to your first visit when we did the Foot Press in sitting and talked about Newton’s 3rd Law? For every action there’s an opposite and equal reaction and, how by pressing your feet down it helped you to sit straighter and gave more support to your back?” She nodded in agreement.
“Well, there’s another important component to that- one that we call optimal alignment. When we sit or stand in a flexed posture, those two opposing forces do not line up well and can put undue stress and pressure on our body, particularly the vertebral bodies.” I showed her the spine again with an increased flexion (hyper-kyphosis) in the thoracic area. “It’s normal to have a kyphosis in the thoracic spine. What we don’t want is a hyper-kyphosis. We often see the apex of the increased curve around T-7, 8, 9 levels near the bra line. We also call it the “slouch line” because from the front, that’s where we slouch in sitting. A thoracic hyper-kyphosis can lead to hyper-lordosis in the lumbar spine as the body tries to counteract the flexion forces above with extension or arching in the low back. We know that Wolff’s Law states that bone in a healthy person will adapt to the loads under which it is placed.1 But we want those loads to be optimally transmitted; otherwise the adaptation can be problematic.”
With Maryanne sitting in a Perch Posture position on the side of the low mat table, I placed a 4 foot dowel rod alongside her back, touching her sacrum and apex of her thoracic curve. I instructed her to bring her occiput back toward the dowel without extending her neck. I wanted her to do more of a cervical retraction move. She was a good 3+ inches away. Previously I had measured her using the WOD (Wall to Occiput Distance).2 This helps patients understand when they are forward flexed in the upper thoracic and cervical area and becomes an exercise as well. Since Maryanne was not safe in a standing position, we used an armless chair against the wall. I turned it sideways so the side of the chair was snugged up to the wall and transferred her to the chair, sitting so that her sacrum was flush against the wall. “Bring your upper back against the wall without allowing your low back to arch forward”, I told her as I placed a folded towel behind her head. “Now you’re going to press the back of your head into the towel, just as you do when lying down in the Re-alignment routine. Before you perform the Head Press, inhale to prepare, start your exhale, then do the head press. Hold for 3 -5 seconds as you continue to exhale, then relax as you inhale. Do 3-5 reps.”
The Head Press in standing, (or in Maryanne’s case, sitting) is a convenient way to not only strengthen the back muscles isometrically, but also increase awareness of body in space and relationship of head to trunk positioning. For any individual who has developed a forward head position over a period of years, there is a loss of the proprioceptive feedback necessary to know when we’re not in alignment, even if we have the ROM to achieve it. And often a lack of strength and especially muscle endurance to maintain that optimally aligned position is problematic. Using the wall several times a day can assist in building strength and awareness. In Maryanne’s case we needed a folded towel behind her occiput to give her something to press into and prevented her from going into increased cervical extension.
“I still want you to do the Head Press in supine as part of the Re-alignment routine everyday”, I told her. “But also practice it in sitting against a wall, making sure your sacrum is right up against it. Do this several times a day for several minutes, holding 3-5 seconds each. And be sure to use your breath to maintain neutral alignment of your lumbar spine.”
And with that, our work for the day was done.
1. Wolff's Law and bone's structural adaptations to mechanical usage: an ... https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8060014
2. Concurrent Validity of Occiput-Wall Distance to Measure Kyphosis in Communities. Journal of Clinical Trials. May 18, 2012 Sawitree Wongsa1,4, Pipatana Amatachaya2,4, Jeamjit Saengsuwan3,4 and Sugalya Amatachaya1,4*
The following is part two in a series documenting Deb Gulbrandson, PT, DPT's journey treating a 72 year old patient who has been living with multiple sclerosis (MS) since age 18. Catch up with Part one of the patient case study on the Pelvic Rehab Report here. Dr. Gulbrandson is a certified Osteoporosis Exercise Specialist and instructor of the Meeks Method, and she helps teach The Meeks Method for Osteoporosis course.
On Maryanne’s second visit, she reported she had been doing her “homework” and didn’t have any questions. Just to be sure, we reviewed them and I had her demonstrate. In Decompression position, she was lying supine with her hands on her abdomen, a common mistake I see. Usually this is due to tightness in pec minor with protracted scapulae. Patients unknowingly resort to the path of least resistance to take the strain off of the muscles. I explained to her that we want to use gravity to gently lengthen those muscles and “widen” the collarbones to allow for improved alignment. With her shoulders abducted to approximately 30 degrees and palms up, I propped a couple of small towels under her forearms which allowed her shoulders to relax into a more posterior and correct position.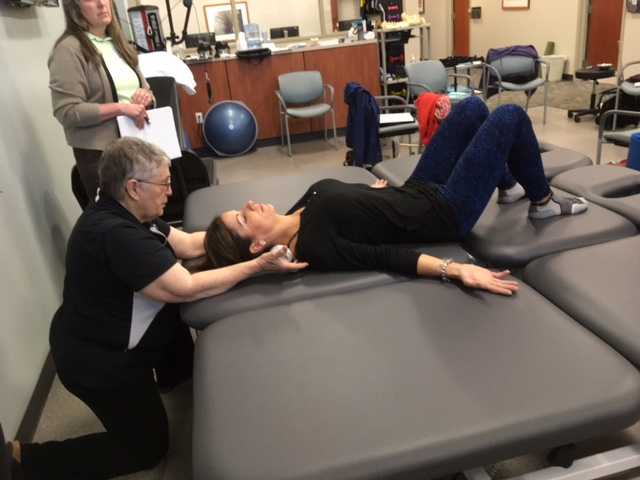
“Today we begin the Re-alignment routine,” I said, “starting with the Shoulder Press.” I showed her how to gently press the back of her shoulders down into the mat without arching her lumbar spine. “As you press your shoulders down, exhale through your mouth as if you’re fogging a mirror. This will help activate your core muscles to keep your back in good alignment. Hold for 2-3 seconds, and then relax. Repeat 3 times.” Maryanne looked at me as if I’d lost my mind. “Did you say do 3 reps?” she asked. “I do 2 sets of 20 reps at the gym,” she said with obvious pride in her voice. “Yes, that’s where we start, and there are a couple of reasons. First, these are very site specific exercises which focus on the exact areas that need strengthening. Exercises done in a gym setting are often more general and usually involve compensation. We are minimizing any compensation such as allowing your low back to arch. There is probably weakness in those upper back muscles as well as the tightness seen in your anterior chest muscles and we need to go slowly. Also, we are simultaneously stretching while we strengthen. Our society is so forward biased (we work on computers, drive cars, make beds, eat- it’s all forward, forward, forward), that the anterior muscles get tight and the upper back muscles get overstretched and weak. We need to reverse that pattern. Take a look at our younger population and their texting postures. Yikes! We will be layering on more exercises as your technique improves so you’ll be doing more than just 3 reps, I promise.”
After the Shoulder Press we proceeded with the Head Press, Leg Lengthener and Arm Lengthener, spending time to make sure her cervical spine stayed in neutral as she pressed her head down into the mat. Head Press (cervical retraction) performed in supine allow patients to have something to press against and helps inhibit the tendency to move into cervical extension. It can also be done standing against the wall with a small pillow or folded towels between the occiput and the wall.
We ended with Maryanne in standing at the kitchen sink to promote functional activities and weight bearing positions. I reminded her to do the Foot Press through the floor using the Triangle of Foot Support visual. This helped to elongate her spine. “Imagine a bungie cord running from the top back of your head to the ceiling” I said which further increased her standing height. “Now I want you to imagine a shelf running straight out from your breastbone with a glass of some very expensive fine drink sitting on it. Do not spill your libation! Oh, and one last thing Maryanne. Breathe!!!” At which point she collapsed into laughter and our session was over. “Busted”, she said.
The expression, “the canary in the coal mine” comes from a long ago practice of coalminers bringing canaries with them into the coalmines. These birds were more sensitive than humans to toxic gasses and so, if they became ill or died, the coalminers knew they had to get out quickly. The canaries were a kind of early warning signal before it was too late. Even though the practice has been discontinued, the metaphor lives on as a warning of serious danger to come.
Osteoporosis, which means porous bones, has been called a silent disease because often an individual doesn’t know he or she has it until they break a bone. The three common areas of fracture are the wrist, the hip, or the spine. Osteoporosis fractures are called fragility fractures, meaning they happen from a fall of standing height or less. We should not break a bone just by a fall unless there is an underlying cause which makes our bones fragile.
 Wrist fractures typically happen when a person starts to fall and puts his or her arms out to catch themselves. They often are seen in the Emergency Department but seldom followed up with an Osteoporosis workup. According to the International Osteoporosis Foundation’s Capture the Fracture program, 80% of fracture patients are never offered screening and / or treatment for osteoporosis. As professionals working with patients who often have co-morbidities, we can be the ones to screen for osteoporosis and balance problems, particularly if our patients have a history of fractures. These screens include the following:
Wrist fractures typically happen when a person starts to fall and puts his or her arms out to catch themselves. They often are seen in the Emergency Department but seldom followed up with an Osteoporosis workup. According to the International Osteoporosis Foundation’s Capture the Fracture program, 80% of fracture patients are never offered screening and / or treatment for osteoporosis. As professionals working with patients who often have co-morbidities, we can be the ones to screen for osteoporosis and balance problems, particularly if our patients have a history of fractures. These screens include the following:
1. Check for the three most common signs of osteoporosis:
a. History of fractures
b. Hyper-kyphosis of the thoracic spine
c. Loss of height equal or greater than 4 cm.
2. Grip Strength
Low grip strength in women is associated with low bone density1
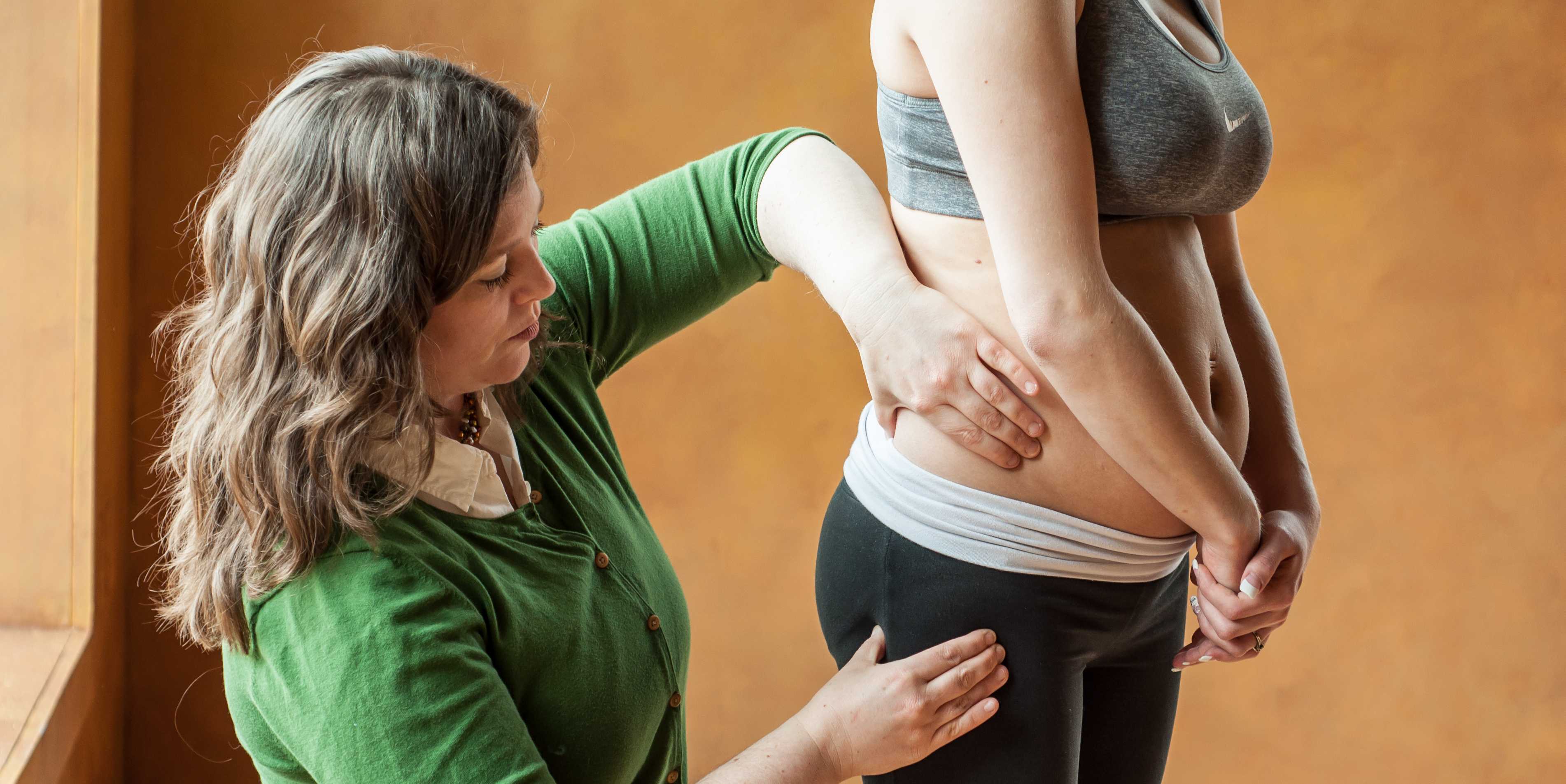
3. Rib-pelvic distance- less than two fingerbreadths.
With the patient standing with their back to you, arms raised to 90 degrees, check the distance from the lowest rib to the iliac crest. Two fingerbreadths or less may be indicative of a vertebral fracture.
A prior fracture is associated with an 86% increased risk of any fracture based on a 2004 meta-analysis by Kanis, Johnell, and De Laet in Bone 2. Fracture predicts fracture. It is our duty as professionals and as human beings to intervene by screening and referring out even if this is not the primary reason we are treating this patient. Fractures from osteoporosis can be devastating, resulting in increased risk of mortality at worst and a diminished quality of life at best. Look for the canaries in the coal mine. Our patients deserve to live the quality of life they envision.
Deb Gulbrandson, PT, DPT, CEEAA teaches the Meeks Method for Osteoporosis Management seminars for Herman and Wallace around the country.
1. Dixon WG et al. Low grip strength is associated with bone mineral density and vertebral fracture in women. Rheumatology 2005;44:642-646
2. Kanis JA, Johnell O, De Laet C, et al. (2004) A meta-analysis of previous fracture and subsequent fracture risk. Bone 35:375
On my son’s due date, I ran 5 miles (as I often did during my pregnancy), hoping he would be a New Year’s baby. The thought of low bone density never crossed my mind, even living in Seattle where the sun only intermittently showers people with Vitamin D. However, bone mineral density changes do occur over the course of carrying a fetus through the finish line of birth. And sometimes women experience a relatively rare condition referred to as pregnancy-related osteoporosis.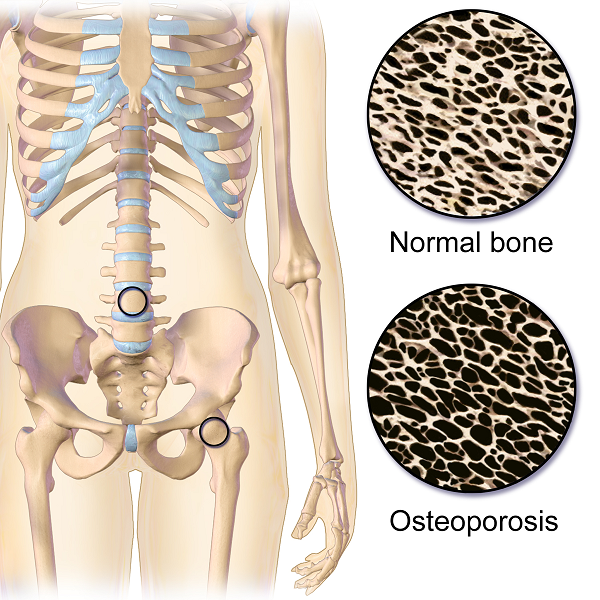
Krishnakumar, Kumar, and Kuzhimattam2016 explored vertebral compression fracture due to pregnancy-related osteoporosis (PAO). The condition was first described over 60 years ago, and risk factors include low body mass index, physical inactivity, low calcium intake, family history, and poor nutrition. Of 535 osteoporotic fractures considered, 2 were secondary to PAO. A 27-year-old woman complained of back pain during her 8th month of pregnancy, and 3 months postpartum, she was found to have a T10 compression fracture. A 31-year-old with scoliosis had back pain at 1 month postpartum but did not seek treatment until 5 months after giving birth, and she had T12, L1, and L2 compression fractures. The women were treated with the following interventions: cessation of breastfeeding, oral calcium 100 mg/day, Vitamin D 800 IU/day, alendronate 70 mg/week, and thoracolumbar orthosis. Bone density improved significantly, and no new fractures developed during the 2-year follow up period.
Nakamura et al.2015 reviewed literature on pregnancy-and-lactation-associated osteoporosis, focusing on 2 studies. The authors explained symptoms of severe low back, hip, and lower extremity joint pain that occur postpartum or in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy can be secondary to this disorder, but it is often not considered immediately. A 30-year-old woman with such debilitating pain in her spine with movement 2 months postpartum had to stop breastfeeding, and 10 months later, she was found to have 12 vertebral fractures. She had low bone mineral density (BMD) in her lumbar spine, and she was given 0.5mg/day alfacalcidol (ALF), an active vitamin D3 analog, as well as Vitamin K. No more fractures developed over the next 6 years. A 37-year-old female had severe back pain 2 months postpartum, and at 7 months was found to have 8 vertebral fractures due to PAO. Her pain subsided after stopping breastfeeding, using a lumbar brace, and supplementing with 0.5mg/day ALF and Vitamin K. The authors concluded goals for treating PAO include preventing vertebral fractures and increasing BMD and overall fracture resistance with Vitamins D and K.
Other treatment approaches for similar case presentations have been published. One gave credit to denosumab injections giving pain relief and improved BMD to 2 women, ages 35 and 33, after postpartum vertebral fractures (Sanchez, Zanchetta, & Danilowicz2016). Guardio and Fiore2016 reported success using the amino-bisphosphonates, neridronate, in a 38-year-old with PAO T4 fracture.
Thankfully for these women experiencing PAO vertebral fractures, supplements boosted their BMD and prevented further fractures. However, they all had to prematurely stop breastfeeding to reduce their pain as well. This rare condition can be used as a warning for women to proactively increase their BMD. The course, Meeks Method for Osteoporosis, can help therapists implement safe, effective, and active ways to promote bone health for all - especially the pregnant population in serious need of support.
Krishnakumar, R., Kumar, A. T., & Kuzhimattam, M. J. (2016). Spinal compression fractures due to pregnancy-associated osteoporosis. Journal of Craniovertebral Junction & Spine, 7(4), 224–227. http://doi.org/10.4103/0974-8237.193263
Nakamura, Y., Kamimura, M., Ikegami, S., Mukaiyama, K., Komatsu, M., Uchiyama, S., & Kato, H. (2015). A case series of pregnancy- and lactation-associated osteoporosis and a review of the literature. Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management, 11, 1361–1365. http://doi.org/10.2147/TCRM.S87274
Sánchez, A., Zanchetta, M. B., & Danilowicz, K. (2016). Two cases of pregnancy- and lactation- associated osteoporosis successfully treated with denosumab. Clinical Cases in Mineral and Bone Metabolism, 13(3), 244–246. http://doi.org/10.11138/ccmbm/2016.13.3.244
Gaudio, A., & Fiore, C. E. (2016). Successful neridronate therapy in pregnancy-associated osteoporosis. Clinical Cases in Mineral and Bone Metabolism, 13(3), 241–243. http://doi.org/10.11138/ccmbm/2016.13.3.241