Tibial nerve stimulation has been shown in the literature to be effective for individuals experiencing idiopathic overactive bladder in randomized controlled trials. A systematic review was performed by Schneider, M.P. et al. in 2015 looking at safety and efficacy of its use in neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction. Many variables were examined in this review, which included 16 studies after exclusion. The review looked at:
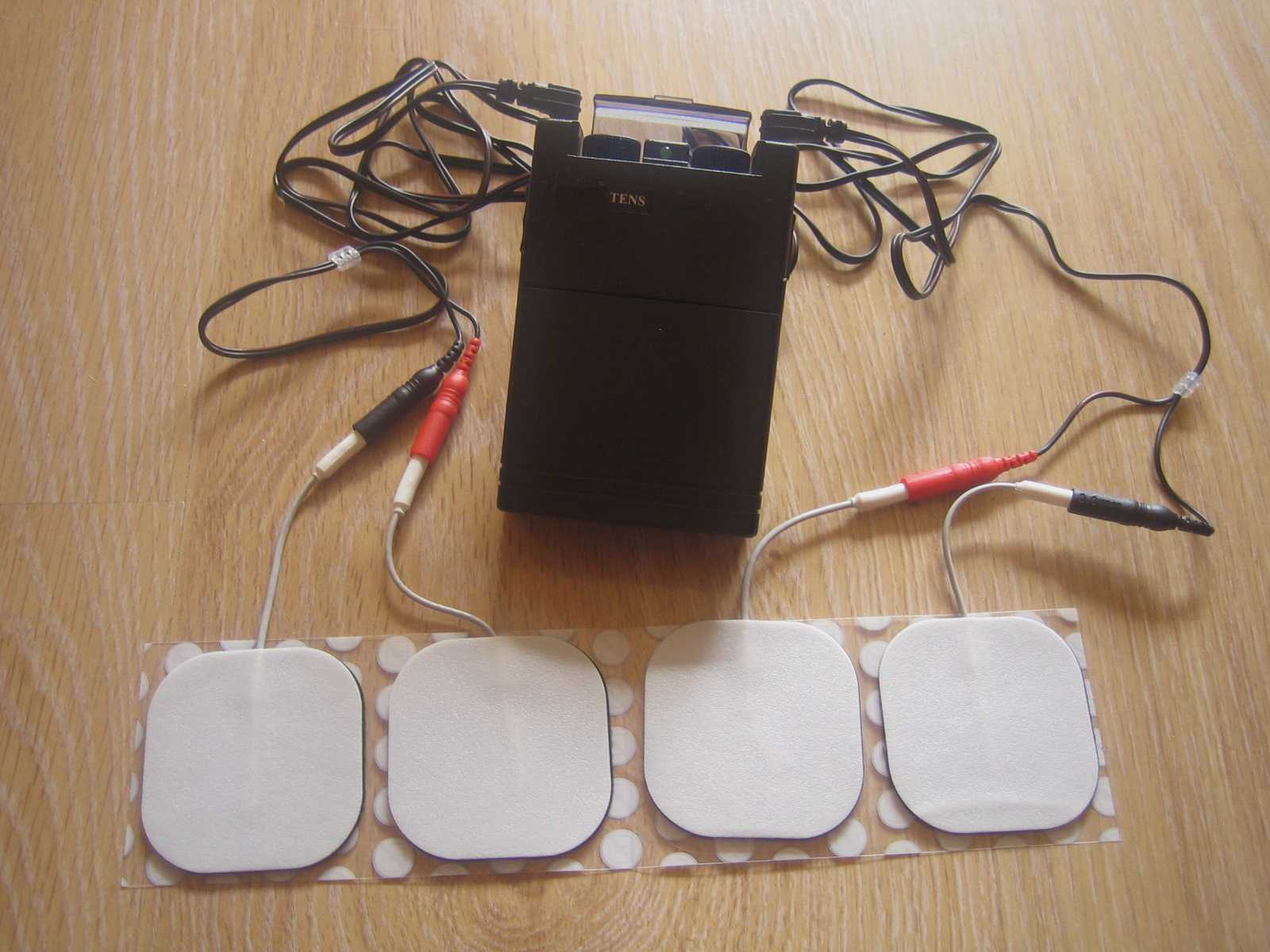
- Acute stimulation (used during urodynamic assessment only)
- Chronic stimulation (6-12 weeks of daily-weekly use)
- Percutaneous or transcutaneous (frequencies, pulse widths, perception thresholds, durations)
- Urodynamic parameter changes baseline to post treatment
- Post void residual changes
- Bladder diary variables
- Patient adherence to tibial nerve stimulation
- Any adverse events
The exact mechanism of these types of neuromodulation stimulation procedures remains unclear, however it does appear to play a role in neuroplastic reorganization of cortical networks via peripheral afferents. No specific literature is currently available for the mechanism on action related to neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction. Different applications of neuromodulation however have been studied in the neurogenic populations.
One of the randomized controlled trials they report on included 13 people with Parkinson disease. The researchers looked at a comparison between the use of transcutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (n = 8) and sham transcutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (n=5). Transcutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (TTNS) or sham stimulation was delivered to the people with Parkinson disease 2x/week for 5 weeks, 30-minute sessions (10 total sessions). Unilateral electrode placement was utilized, first electrode applied below the left medial malleolus and second electrode 5 cm cephalad. Confirmation of placement was obtained with left great toe plantar flexion. It is important to note the use of the stimulation intensity is reduced to below the motor threshold during the active treatment to direct the stimulation via peripheral afferents.
Urodynamic testing was performed at baseline and post treatment and revealed statistically significant differences with greater volumes at strong desire and urgency in the TTNS group. Additionally, the TTNS group experienced a 50% reduction in nocturia whereas in the sham group nocturia frequency remained the same. A three-day bladder diary completed by each of the groups also revealed significant positive changes in frequency, urgency, urge urinary incontinence and hesitancy only in the TTNS group.
Conservative management of neurogenic bladder in populations such as Parkinson disease is very important. These individuals experience lower quality of life ratings related to lower urinary tract dysfunction, higher risk of falling with needs to rush to the bathroom, their caregivers experience a higher level stress and burden of care, and tolerance to anticholinergic medications is very poor with multiple unwanted side effects that compound and worsen other symptoms that might be present from the disease process.
Please join us for Neurologic Conditions and Pelvic Floor Rehab to learn how you can help your patients using this modality as one option. Participate in a lab session to learn electrode placement and other parameters to achieve best clinical results for your patients.
1. Perissinotto, M. C., D'Ancona, C. A. L., Lucio, A., Campos, R. M., & Abreu, A. (2015). Transcutaneous tibial nerve stimulation in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms and its impact on health-related quality of life in patients with Parkinson disease: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Wound Ostomy & Continence Nursing, 42(1), 94-99.
2. Schneider, M. P., Gross, T., Bachmann, L. M., Blok, B. F., Castro-Diaz, D., Del Popolo, G., ... & Kessler, T. M. (2015). Tibial nerve stimulation for treating neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction: a systematic review. European urology, 68(5), 859-867.
The following is the first in a series on self-care and preventing practitioner burnout from faculty member Jennafer Vande Vegte, MSPT, BCB-PMD, PRPC. Jennafer is the co-author and co-instructor of the Boundaries, Self-Care, and Meditation course along with Nari Clemons, PT, PRPC.
Part 1: Boundaries
“I just want you to fix me.” How many times have we heard this statement from our patients? And how do we respond? In my former life as a “rescuer” this statement would be a personal challenge. I wanted to be the fixer, find the solution and identify the thing that no one else had seen yet. Then, if I am being completely honest, bask in the glory of being the “miracle worker” and “never giving up” on my patient.
 If you recognize that this attitude was going to run me into some problems, kudos to you. If you are thinking, “well of course, isn’t that your job as a pelvic floor physical therapist?” Please read on.
If you recognize that this attitude was going to run me into some problems, kudos to you. If you are thinking, “well of course, isn’t that your job as a pelvic floor physical therapist?” Please read on.
On my very first job performance review, when it came time to discuss my problem areas my supervisor relayed I was “too nice” and cited some examples: giving a patient a ride home after therapy (it was raining and she would have had to wait for the bus), coming in on Saturdays to care for patients (he was sick and couldn’t make it in during the week but was making really good progress). You get the picture. At the time, I didn’t understand how this could be something I needed to work on. I was going above and beyond and I got so much satisfaction from taking care of others!
Fast forward 10 years and add to my life a husband, two daughters, a teaching job, part time homeschooling, and writing course material. I was an emotional mess. Anxiety was my permanent state of mind. I gave my best to my patients while my family got my meager emotional leftovers. Something had to change and luckily it did. I got help and learned exactly what boundaries are and how to develop as well as enforce them.
There are several resources that discuss professional boundaries in health care, like this from Nursing Made Incredibly Easy. In this particular article, health care professionals are exhorted to stay in the “zone of helpfulness” and avoid becoming under involved or over involved with patients. Health care professionals are also urged to examine their own motivation. Am I using my relationship with my patient to fulfill my own needs? Am I over involved so that I can justify my own worth?
Here are some warning signs that you are straying away from healthy boundaries with patients and becoming over involved:
- Discussing your intimate or personal issues with a patient
- Spending more time with a patient than scheduled or seeing a patient outside of work
- Taking a patient's side when there's a disagreement between the patient and his or her close relations
- Believing that you are the only health care member that can help or understand a patient
For some people, certain patients who push professional boundaries will cause the therapist to feel threatened and under activity is the result. This might result in talking badly about the patient to other staff, distancing ourselves, showing disinterest in their case, or failing to utilize best care practices for the patient.
Per Remshard 2012, “When you begin to feel a bit detached, stand back and evaluate your interactions. If you sense that boundaries are becoming blurred in any patient care situation, seek guidance from your supervisor. A sentinel question to ask is: ‘Will this intervention benefit the patient or does it satisfy some need in me?’”
Healthy professional boundaries are imperative for us and for our patients. Boundaries also help prevent burnout. Remshard delineates what healthy boundaries look like:
- Treat all patients, at all times, with dignity and respect.
- Inspire confidence in all patients by speaking, acting, and dressing professionally.
- Through your example, motivate those you work with to talk about and treat patients and their families respectfully.
- Be fair and consistent with each patient to inspire trust, amplify your professionalism, and enhance your credibility.
If you struggle with professional and personal boundaries, you are not alone and you can get support. Consider talking with your supervisor, a counselor, reading a good book on the subject or taking Boundaries, Self-Care, and Meditation, a course offering through Herman and Wallace that was designed to help pelvic health professionals stay healthy and inspired while equipping therapists with new tools to share with their patients.
We hope you will join us for Boundaries, Self-Care, and Meditation this November 9-11, 2019 in San Diego, CA.
Look forward to my next blog where The Rescuer (me) needs Rescuing and learn about the Drama Triangle.
Remshardt, Mary Ann EdD, MSN, RN "Do you know your professional boundaries?" Nursing Made Incredibly Easy!: January/February 2012 - Volume 10 - Issue 1 - p 5–6 doi: 10.1097/01.NME.0000406039.61410.a5
Diagnosing sacroiliac joint (SIJ) dysfunction can be tricky. Therapists need to rule out lumbar spine and the hip, and sometimes there is more than one area causing pain and limiting functional mobility. Typically, ruling in SIJ dysfunction is done by pain provocation tests and load transfer tests. Once the SIJ has been ruled in, then therapists can use a variety of treatments. Often those treatments include therapeutic exercise, joint manipulation, and Kinesio tape. But which intervention is the most effective?
A recent study looked at three physical therapy interventions for treatment for SIJ (sacroiliac joint) dysfunction and assessed which was the most effective (Al-Subahi, M 2017). The authors did a systematic review of the literature. The articles were from 2004-2014, written in English, with male and female participants. This review included a variety of experiment types from randomized control trials to case studies. Of the 1114 studies, only 9 met the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Four of the nine studies used manipulation, three used Kinesio Tape, and the three used exercise. One study did both exercise and manipulation, and was looked at in both interventions. All categories had at least one randomized control trial.
For the manipulation intervention, all studies showed a decrease in pain and disability at follow up. The follow ranged from 3 to 4 days to 8 weeks. Disability was measured using the Oswestry Disability Index. One study did manual high velocity and low amplitude thrust manipulation to lumbar and SIJ manipulation and showed improvement with manipulation to SIJ or SIJ and lumbar. The review did not disclose the type of lumbar manipulation, but did state the SIJ manipulation was a side bend and rotation position with an inferior and lateral force to ASIS (anterior superior iliac spine). Another study did either a SIJ manual high velocity and low amplitude thrust manipulation or a mechanical force with manual assistance. One studied did manipulation and home exercises but did not record exercise interventions. The last study did the same SIJ manual high velocity and low amplitude thrust manipulation as in previous study combined with exercise. The exercises are mentioned below.
For the exercise intervention, the studies did primarily stabilization exercises that were either isometric or isotonic eccentric or concentric. Quick PT school review, in isometric exercises the muscle does not change length, while in isotonic eccentric exercises the muscle is being lengthened under load, and isotonic concentric is the muscle shortening under load. All three studies showed decrease in pain. The first study had 7 participants and combined manipulation and exercise. The exercises consisted of 12% max voluntary contraction and eccentric loading quads in supine with hips at 90 degrees, and concentrically loading hamstrings in prone. The second study was a case study and performed 8 lumbo-pelvic-femoral stabilization exercises for 8 weeks. Fun fact: this case study was written by my Therapeutic Exercise teacher in PT school who did a lot of Postural Restoration based exercises. The last study, had 22 participants and educated and provided exercises on deep abdominal and multifidus muscles and do complete these exercises during functional movements throughout the day. These participants were follow up a year later and had decreased pain compared to laser group.
For the Kinesio tape (Kinesio tape) intervention, the studies did not find that Kinesio tape was not an effective intervention, however the follow up ranged from immediately after applying tape to 4 weeks afterwards. In the first study, a randomized controlled trial with 60 participants, the Kinesio tape was applied in sitting with 25% tension of 4 strips making a star pattern over the point of maximal pain. The Kinesio tape was compared to placebo tape and showed equal improvement in pain and disability. The other two studies applied a different taping technique where the Kinesio tape was applied. One applied the tape over erector spinae and internal oblique muscles bilaterally and in the other study the Kinesio tape was applied with 25% tension over external obliques, a second strip was placed from ASIS to PSIS in side-lying, and then a third strip was placed along rectus abdominis muscle. In this same study the tape was applied for weeks (6x/week for 9 hours/day).
In summary, the authors note that all three interventions help decrease pain and disability in women and men with SIJ dysfunction. The authors suggest that manipulation may be the most effective. Kinesio tape showed no significant difference between placebo tape. Exercise was effective, but less so than manipulation.
This review has a lot of limitations. The variety of experiment types with varying degrees of evidence, small number of participants, and lack of blinding. Most studies had a limited follow up ranging from 3-4 days to 12 months. The outcome measures varied greatly. Most studies had pain scores as the outcome measure, though one study only used inclination meter of anterior pelvic tilt. Use of a consistent objective measure in addition to perceived pain and disability would have helped. Only 1 study did pain provocation tests and that study was a case study whose intervention focused on Kinesio-taping.
As physical therapists we want to provide effective evidence-based practice, and we want to provide individualized compassionate care. It is hard to make a direct line between this study’s recommendations and clinical application based on the numerous limitations. I agree with the authors that manipulation and exercise are bread and butter to physical therapists. I disagree about Kinesio tape not being an effective treatment. Is Kinesio tape going to create boney alignment changes? Likely not. Is Kinesio tape (or any other tape) going to give proprioceptive feedback and possibly help calm sensory pathways? Yes. If a patient likes being taped, and thinks it will help, then I will tape them. Even if taping is just placebo effect; it’s still an effect.
Al-Subahi, M., Alayat, M., Alshehr, M.A., et al. (2017) The effectiveness of physiotherapy interventions for sacroiliac joint dysfunction: A systematic review. J Phys. Ther. Sci. 29: 1689-1694.
Rehabilitative ultrasound imaging has been used in clinical practice for well over a decade now. It has been used for core stabilization, as well as with female incontinence patients. In recent years, transperineal ultrasound imaging has emerged as a useful tool for assessing prolapses and identifying other women’s health issues in the anterior compartment.
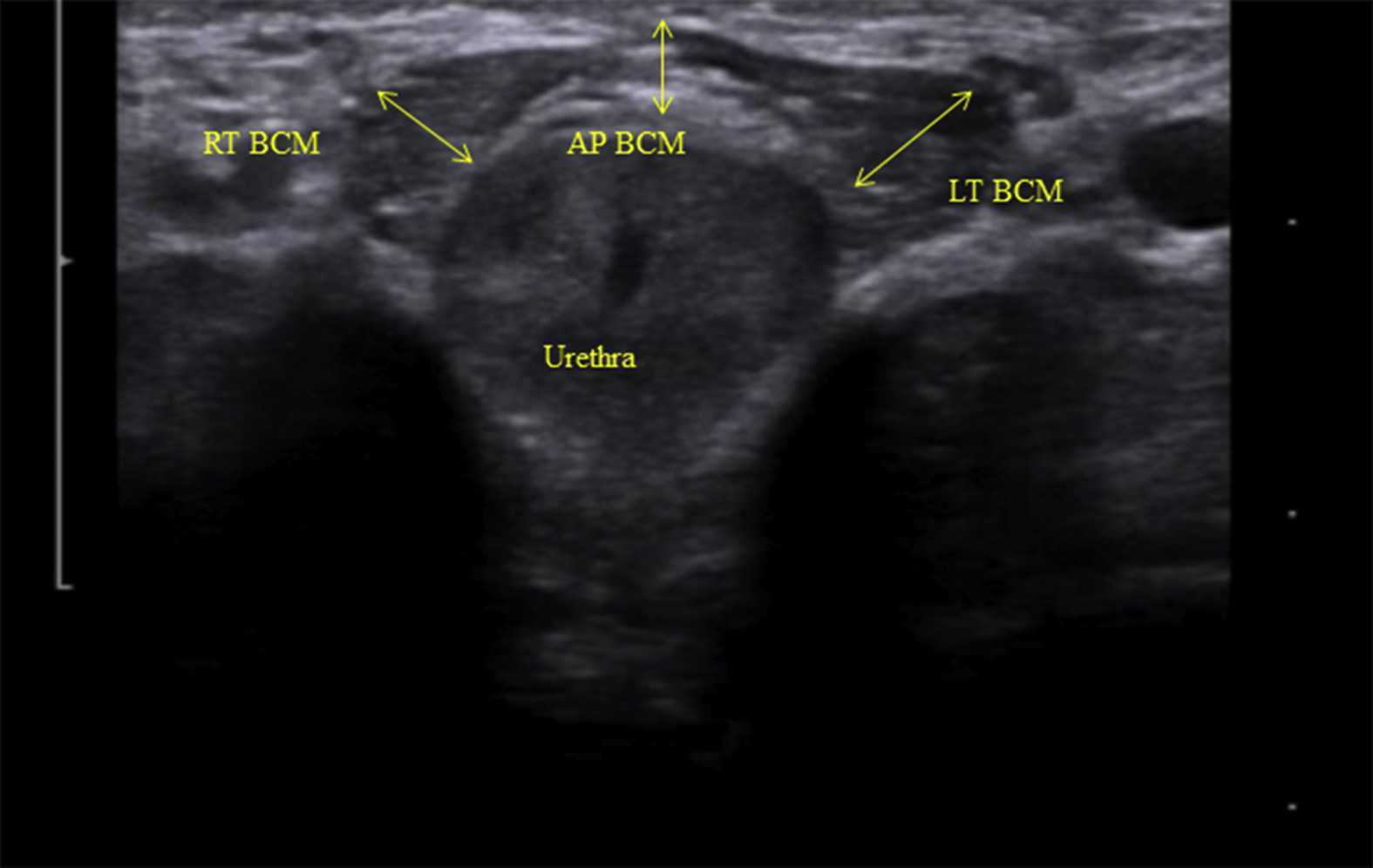 Like other things in men’s pelvic health, the use of ultrasound imaging for rehabilitation has lagged behind that in women’s pelvic health. Ryan Stafford is a researcher that is working to change that. In 2012, Stafford began looking at the normal responses to pelvic floor contractions and what is seen on ultrasound in men. He has since taken his research further to examine differences in men that present with post-prostatectomy incontinence. Stafford, van den Hoorn, Coughlin, and Hodges performed a study looking at the dynamic features of activation of specific pelvic floor muscles, and anatomical parameters of the urethra. The study included forty-two men who had undergone prostatectomy. Some of these men were incontinent and others remained continent. Transperineal ultrasound imaging was used to obtain images of the pelvic structures during a cough, and a sustained maximal contraction. The research team calculated displacements of pelvic floor landmarks with contraction, as well as anatomical features including urethral length, and resting position of the ano-rectal and urethra-vesical junctions.
Like other things in men’s pelvic health, the use of ultrasound imaging for rehabilitation has lagged behind that in women’s pelvic health. Ryan Stafford is a researcher that is working to change that. In 2012, Stafford began looking at the normal responses to pelvic floor contractions and what is seen on ultrasound in men. He has since taken his research further to examine differences in men that present with post-prostatectomy incontinence. Stafford, van den Hoorn, Coughlin, and Hodges performed a study looking at the dynamic features of activation of specific pelvic floor muscles, and anatomical parameters of the urethra. The study included forty-two men who had undergone prostatectomy. Some of these men were incontinent and others remained continent. Transperineal ultrasound imaging was used to obtain images of the pelvic structures during a cough, and a sustained maximal contraction. The research team calculated displacements of pelvic floor landmarks with contraction, as well as anatomical features including urethral length, and resting position of the ano-rectal and urethra-vesical junctions.
The data was analyzed and combinations of variables that best distinguished men with and without incontinence were reported. Several important components were identified in the study. Striated urethral sphincter activation, as well as bulbocavernosus and puborectalis muscle activation were significantly different between men with and without incontinence. When these two parameters were examined together, they were able to correctly identify 88.1% of incontinent men. They further reported that poor function of the puborectalis and bulbocavernosus could be compensated for if the man had good striated urethral sphincter function. However, the puborectalis and bulbocavernosus had less potential to compensate for poor striated urethral sphincter function. This is important for a therapist that works with post prostatectomy patients to know. This can explain part of why some men improve and do so well after a prostatectomy and others don’t, even with therapy to help. If the striated urethra sphincter is damaged and its normal responses are changed during surgery, then incontinence after prostatectomy may be more likely.
Using ultrasound imaging, the therapist can examine and see exactly where a man is deficient in response; whether it is the puborectalis, or the striated urethra sphincter. It is exciting to see this new research and see how rehabilitative ultrasound imaging can influence men’s pelvic health! Come and learn how to use ultrasound imaging for your men’s pelvic health patients as well as your women’s health and back pain patients! You will see how ultrasound imaging can change your practice and how much your patients will enjoy seeing real-time images of their contractions! Thanks to our partnership with The Prometheus Group, this course includes hands-on training on the latest in pelvic ultrasound imaging.
1. Stafford R, Ashton-Miller J, Constantinou C, et al. Novel insights into the dynamics of male pelvic floor contractions through transperineal ultrasound imaging. J. Urol. 2012; 188: 1224-30.
2. Stafford RE, van den Hoorn W, Couglin G, Hodges P. Postprostatectomy incontinence is related to pelvic floor displacements observed with trans-perineal ultrasound imaging. Neurol and Urodyn. 2018; 37:658-665.
Image credit Gupta et al. 2016 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajur.2016.11.002 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2214388216300881#fig2
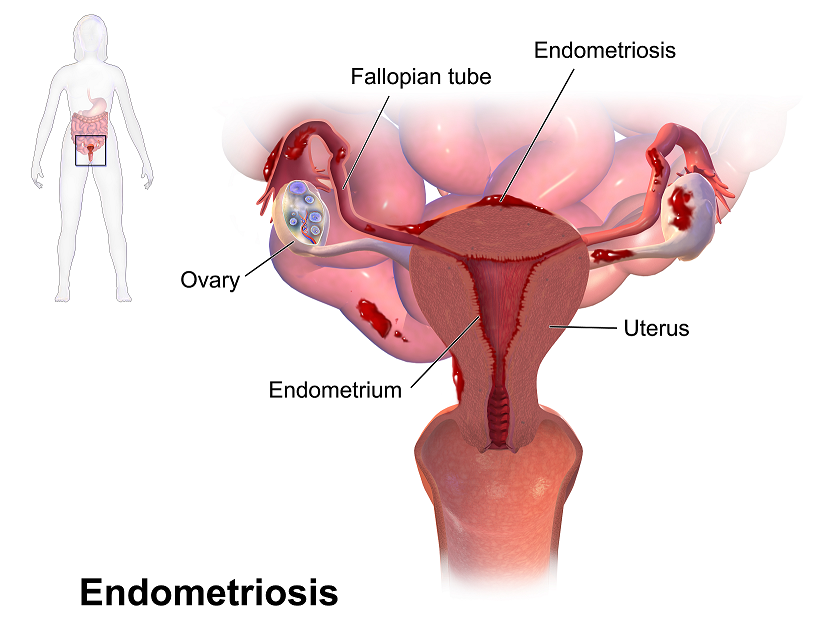
Recent data suggests that there are about 4 million American women diagnosed with endometriosis, but that 6/10 are not diagnosed. Currently, using the gold standard for diagnosis there are potentially 6 million American woman that may experience the sequelae of endometriosis without having appropriate management or understanding the cause of their symptoms.
The gold standard for endometriosis is laparoscopy either with or without histologic verification of endometrial tissue outside of the uterus. However, there is a poor correlation between disease severity and symptoms. The Agarwal et al study suggests a shift to focus on the patient rather than the lesion and that endometriosis may better be defined as “menstrual cycle dependent, chronic, inflammatory, systemic disease that commonly presents as pelvic pain”. There is often a long delay in symptom appreciation and diagnosis that can range from 4-11 years. The side effects of this delay are to the detriment of the patient; persistent symptoms and effect of quality of life, development of central sensitization, negative effects on patient-physician relationship. If this disease continues to go untreated it may affect fertility and contribute to persistent pelvic pain.
 The authors suggest a clinical diagnosis with transvaginal ultrasound for patients presenting with persistent or cyclic pelvic pain, patient history, have symptoms consistent with endometriosis, or other findings suggestive of endometriosis. The intention of using transvaginal ultrasound is to make diagnosis more accessible and limit under diagnosis. It is not intended to minimize laparoscopy as a diagnostic tool or treatment option.
The authors suggest a clinical diagnosis with transvaginal ultrasound for patients presenting with persistent or cyclic pelvic pain, patient history, have symptoms consistent with endometriosis, or other findings suggestive of endometriosis. The intention of using transvaginal ultrasound is to make diagnosis more accessible and limit under diagnosis. It is not intended to minimize laparoscopy as a diagnostic tool or treatment option.
The algorithm for a clinical diagnosis evaluates patient presentation of the following:
- Symptoms including persistent or cyclic pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea or painful menstruation cramps, deep dyspareunia or pain with deep vaginal penetration, cyclic dyschezia or straining for soft stools, cyclic dysuria or pain with urination, cyclic catamenial symptoms located in other systems such as acne or vomiting.
- Assessment of patient history including infertility, current chronic pelvic pain, or painful periods as an adolescent, previous laparoscopy with diagnosis, painful periods that are not responsive to NSAIDS, and a family history.
- Physical exam physicians assess for nodules in cul de sac, retroverted uterus, mass consistent with endometriosis, visible or obvious external endometrioma. Imaging should be ordered or performed.
- Clinical signs would consist of endometrioma with US, presence of soft markers (sliding sign) this is where the fundus of the uterus is compared to its neighboring structures and can indicate the immobility of those structures, and nodules or masses.
Of course, there are differential diagnosis for endometriosis, and those are symptoms of non-cyclical patterns of pain and bladder/bowel dysfunction that would indicate IBS, UTI, IC/PBS. A history of post-operative nerve entrapment of adhesions. Examination positive for pelvic floor spasm, severe allodynia in vulva and pelvic floor, masses such as fibroids. It is important to note that these other diagnoses can coexist with endometriosis and do not rule out possible endometriosis diagnosis.
Hopefully, diagnosing individuals earlier and possibly at a younger age would limit the disease severity and symptoms. This would allow this population to limit the possibility of central sensitization and pain persistence that can affect so much of daily life. Earlier diagnosis may affect infertility and allow this population to make informed decisions about family and career from a place of empowerment.
Agarwal SK, Chapron C, Giudice LC, Laufer MR, Leyland N, Missmer SA,Singh SS, Taylor HS, "Clinical diagnosis of endometriosis: a call to action", American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology (2019), doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2018.12.039.
The following is a guest submission from Alysson Striner, PT, DPT, PRPC. Dr. Striner became a Certified Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner (PRPC) in May of 2018. She specializes in pelvic rehabilitation, general outpatient orthopedics, and aquatics. She sees patients at Carondelet St Joesph’s Hospital in the Speciality Rehab Clinic located in Tucson, Arizona.
Myofascial pain from levator ani (LA) and obturator internus (OI) and connective tissues are a frequent driver of pelvic pain. As pelvic therapists, it can often be challenging to decipher whether pain is related to muscular and/or fascial restrictions. A quick review from Pelvic Floor Level 2B; overactive muscles can become functionally short (actively held in a shortened position). These pelvic floor muscles do not fully relax or contract. An analogy for this is when one lifts a grocery bag that is too heavy. One cannot lift the bag all the way or extend the arm all the way down, instead the person often uses other muscles to elevate or lower the bag. Over time both the muscle and fascial restrictions can occur when the muscle becomes structurally short (like a contracture). Structurally short muscles will appear flat or quiet on surface electromyography (SEMG). An analogy for this is when you keep your arm bent for too long, it becomes much harder to straighten out again. Signs and symptoms for muscle and fascial pain are pain to palpation, trigger points, and local or referred pain, a positive Q tip test to the lower quadrants, and common symptoms such as urinary frequency, urgency, pain, and/or dyspareunia.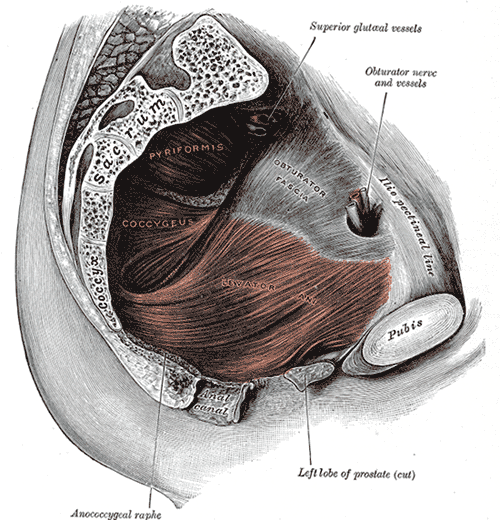
For years in the pelvic floor industry there has been notable focus on vocabulary. Encouraging all providers (researchers, MDs, and PTs) to use the same words to describe pelvic floor dysfunction allowing more efficient communication. Now that we are (hopefully) using the same words, the focus is shifting to physical assessment of pelvic floor and myofascial pain. If patients can experience the same assessment in different settings then they will likely have less fear, and the medical professionals will be able to communicate more easily.
A recent article did a systematic review of physical exam techniques for myofascial pain of pelvic floor musculature. This study completed a systematic review for the examination techniques on women for diagnosis of LA and OI myofascial pain. In the end, 55 studies with 9460 participants; 99.8% were female, that met the inclusion and exclusion criteria were assessed. The authors suggest the following as good foundation to begin; but more studies will be needed to validate and to further investigate associations between chronic pelvic pain and lower urinary tract symptoms with myofascial pain.
The recommended sequence for examining pelvic myofascial pain is:
- Educate patient on examination process. Try to ease any anxiety they may have. Obtain consent for an examination
- Ask the patient to sit in lithotomy position
- Insert a single, gloved, lubricated index finger into the vaginal introitus
- Orient to pelvic floor muscles using clock face orientation with pubic symphysis at 12 o'clock and anus at 6 o'clock
- Palpate superficial and then deep pelvic floor muscles
- Palpate the obturator internus
- Palpate each specific pelvic floor muscle and obturator internus; consider pressure algometer to standardize amount of pressure
Authors recommend bilateral palpation and documentation of trigger point location and severity with VAS. They recommend visual inspection and observation of functional movement of pelvic floor muscles.
The good news is that this is exactly how pelvic therapists are taught to assess the pelvic floor in Pelvic Floor Level 1. This is reviewed in Pelvic Floor Level 2B and changed slightly for Pelvic Floor Level 2A when the pelvic floor muscles are assessed rectally. Ramona Horton also teaches a series on fascial palpation, beginning with Mobilization of the Myofascial Layer: Pelvis and Lower Extremity. I agree that palpation should be completed bilaterally by switching hands to make assessment easier for the practitioner who may be on the side of the patient/client depending on the set up. This is an important conversation between medical providers to allow for easy communication between disciplines.
Meister, Melanie & Shivakumar, Nishkala & Sutcliffe, Siobhan & Spitznagle, Theresa & L Lowder, Jerry. (2018). Physical examination techniques for the assessment of pelvic floor myofascial pain: a systematic review. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 219. 10.1016/j.ajog.2018.06.014
In this post, we want to give a high-level overview of interstitial cystitis and an introduction to other resources if you’d like to dive deeper into treatment the condition. There’s a printable, patient-friendly version of this overview if you’d like to use it in describing the condition with patients. In addition, you may want to review the 8 Myths of Interstitial Cystitis series and the AUA Guidelines for Interstitial Cystitis.
Definition
Interstitial cystitis is defined as pain or pressure perceived to be related to the urinary bladder, associated with lower urinary tract symptoms of more than six weeks duration, in the absence of infection or other identifiable causes.
Unfortunately, for physicians, pelvic floor dysfunction falls under category of ‘unidentifiable cause.’ Interstitial cystitis is really more of a description of symptoms, rather than a discrete diagnosis, and the condition presents in many different ways.

Symptoms
The hallmarks of interstitial cystitis are pelvic pain, often in the suprapubic area or inner thighs, and urinary urgency and frequency. Other common symptoms include pain with intercourse, nocturia, low back pain, constipation, and urinary retention.
Many patients are surprised to realize that symptoms like painful intercourse, low back pain, and constipation are related to their IC diagnosis. This challenges the misconception that issues are arising solely from the bladder, and is a good way to help patients (and their physicians) understand that IC is about more than just the bladder.
Diagnosis
Interstitial cystitis is fundamentally a diagnosis of exclusion. Most patients suspect a urinary tract infection (UTI) when their symptoms first present. It’s actually common for symptoms to start as the result of a UTI, and simply not resolve once the infection has cleared. Patients are often treated with multiple rounds of antibiotics for these ‘phantom’ UTIs, where cultures have come back negative, before an IC diagnosis is considered.
It’s important for us as physical therapists to be able to share with patients that no testing is required to confirm an IC diagnosis, it can be diagnosed clinically. In practice, a urologist will likely want to conduct a cystoscopy, which can rule out more serious issues like bladder cancer as well as check for Hunner’s lesions (wounds in the bladder that are present in about 10% of IC patients). However, after that, no additional testing is needed. The potassium sensitivity test (PST) was formerly used by some urologists, but it has been shown to be useless diagnostically and extremely painful for patients and is not recommended by the American Urological Association. Urodynamic testing is also often conducted, but again is not necessary to establish an IC diagnosis.
Physical Therapy for IC
According to the American Urological Association, physical therapy is the most proven treatment for interstitial cystitis. It’s given an evidence grade of ‘A’ (the only treatment with that grade) and recommended in the first line of medical treatment.
In controlled clinical trials, manual physical therapy has been shown to benefit up to 85% of both men and women. These trials reported benefits after ten visits of one-hour treatment sessions.
In a study conducted at our clinic , PelvicSanity, we found that physical therapy was able to reduce pain for IC patients from an average of 7.6 (out of 10) before treatment to 2.6 following physical therapy. Similarly, how much their symptoms bothered patients fell from 8.3 to 2.8. More than half of patients reported improvements within the first three visits.
Unfortunately, many patients still aren’t referred to pelvic physical therapy by their physician. More than half of the patients in the study had seen more than 5 physicians before finding pelvic PT, and only 7% of patients felt they had been referred to physical therapy at the appropriate time by their doctor.
Multi-Disciplinary Approach
Patients with interstitial cystitis or pelvic pain always benefit from a multidisciplinary approach to treatment.This can include:
- Stress relief to downregulate the nervous system can decrease symptoms and reduce flares. Gentle exercise, meditation, yoga, deep breathing, or working with a psychologist can all provide benefits for patients.
- Diet and nutrition are important when working with IC patients. There is no formal ‘IC Diet’, but most patients are sensitive to at least a few trigger foods. The gold standard of treatment is an elimination diet, where the common culprits are completely removed from the diet and then added back in one at a time. This identifies which foods are triggers for patients. With nutrition for IC, patients should avoid their personal trigger foods and eat healthy – it doesn’t have to be any more restrictive or complicated.
- Alternative treatments like acupuncture have been shown to reduce pelvic pain in patients, and several supplements have shown benefits in trials or anecdotally among patients.
- Bladder treatments include instillations and nerve stimulation. Some patients may benefit from bladder instillations, but many others find that the process of the instillation actually causes additional symptoms. If instillations are beneficial, patients should be encouraged to address the underlying issues during the reprieve that instillations bring. Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation or an implanted nerve stimulation device can both be possible treatment options.
- Oral medications can also reduce symptoms, but do not address the underlying cause of symptoms in patients. Medication that dampens the nervous system, often an anti-depressant or similar medication, can reduce pain and hypersensitivity. Anti-inflammatories may be beneficial in lowering inflammation and helping break the cycle of dysfunction-inflammation-pain. Most patients are started on Elmiron®, the only FDA-approved medication for IC; unfortunately, in the most recent clinical trial research Elmiron has been shown to be no more effective than a placebo. If it is effective, it only is beneficial for about one-third of patients, and many won’t be compliant with the drug due to cost and side effects.
 Nicole Cozean, PT, DPT, WCS (www.pelvicsanity.com/about-nicole) is the founder of PelvicSanity physical therapy in Southern California. Name the 2017 PT of the Year by the ICN, she’s the first physical therapist to serve on the Interstitial Cystitis Association’s Board of Directors and the author of the award-winning book The IC Solution (www.pelvicsanity.com/the-ic-solution). She teaches at her alma mater, Chapman University, as well as continuing education through Herman & Wallace. Nicole also founded the Pelvic PT Huddle (www.facebook.com/groups/pelvicpthuddle), an online Facebook group for pelvic PTs to collaborate.
Nicole Cozean, PT, DPT, WCS (www.pelvicsanity.com/about-nicole) is the founder of PelvicSanity physical therapy in Southern California. Name the 2017 PT of the Year by the ICN, she’s the first physical therapist to serve on the Interstitial Cystitis Association’s Board of Directors and the author of the award-winning book The IC Solution (www.pelvicsanity.com/the-ic-solution). She teaches at her alma mater, Chapman University, as well as continuing education through Herman & Wallace. Nicole also founded the Pelvic PT Huddle (www.facebook.com/groups/pelvicpthuddle), an online Facebook group for pelvic PTs to collaborate.
Interstitial Cystitis Course
In our upcoming course for physical therapists in treating interstitial cystitis (April 6-7, 2019 in Princeton, New Jersey), we’ll focus on the most important physical therapy techniques for IC, home stretching and self-care programs, and information to guide patients in creating a holistic treatment plan. The course will delve into how to handle complex IC presentations. It’s a deep dive into the condition, focusing not just on manual treatment techniques but also how to successfully manage an IC patient from beginning to resolution of symptoms.
Additional Resources
- Interstitial Cystitis Overview (printable)
- The Interstitial Cystitis Solution
- Patient groups include the Interstitial Cystitis Association (ICA) (www.ic-help.org) and the IC Network (www.ic-network.com), which both have fantastic resources for patients.
- The AUA Guidelines for IC
- IC Flare-Busting Plan
Birthing can be an unpredictable process for mothers and babies. With cases of fetal distress, the baby can require rapid delivery. Alternatively, in cases with cephalo-pelvic disproportion, the baby has a larger head, or the mother has a decreased capacity within the pelvis to allow the fetus to travel through the birthing canal. Additionally, the baby may have posterior presentation, colloquially known as “sunny side up” in which the baby’s occipital bone is toward the sacrum. With any of these situations, it is good to know c-sections are an option to safely deliver the child.
 Women may also be inclined to try to get a c-section to avoid pelvic complication or tears or because of a history of a severe prior tear. As pelvic therapists, we know that the number of vaginal births and history of vaginal tears increase the risk of urinary incontinence and prolapse. Yet, many therapists are unfamiliar with the effects of c-section and the impact of rehab for diastasis.
Women may also be inclined to try to get a c-section to avoid pelvic complication or tears or because of a history of a severe prior tear. As pelvic therapists, we know that the number of vaginal births and history of vaginal tears increase the risk of urinary incontinence and prolapse. Yet, many therapists are unfamiliar with the effects of c-section and the impact of rehab for diastasis.
A 2008 dissection study of 37 cadavers studied the path of the ilioinguinal and Iliohypogastric nerves. The course of the nerves was compared with standard abdominal surgical incisions, including appendectomy, inguinal, pfannestiel incisions (the latter used in cesarean sections). The study concluded that surgical incisions performed below the level of the anterior superior iliac spines (ASIS) carry the risk of injury to the ilioinguinal and iloiohypogastric nerves 1. Another 2005 study reported low transverse fascial incision risk injury to the ilioinguinal and Iliohypogastric nerves, and the pain of entrapment of these nerves may benefit from neurectomy in recalcitrant cases.2
Why does injury to the nerves matter? After pregnancy, patients may need rehab and retraining of their abdominal recruitment patterns for diastasis and stability. The ilioinguinal and Iliohypogastric nerves are the innervation for both the transverse abdominus and the obliques below the umbilicus. When we are working to retrain the muscles, certainly neural entrapment or poor firing can greatly impact the success of our intervention as rehab professionals. Interestingly, a study from Turkey showed patients had a significant increase in diastasis recti abdominis (DRA) with a history of 2 cesarean sections and increased parity and recurrent abdominal surgery increase the risk of DRA.2
A fourth study looked at 23 patients with ilioinguinal and Iliohypogastric nerve entrapment syndrome following transverse lower abdominal incision (such as a c-section). In this study, the diagnostic triad of ilioinguinal and Iliohypogastric nerve entrapment after operation was defined as 1) typical burning or lancinating pain near the incision that radiates to the area supplied by the nerve, 2). Clear evidence of impaired sensory perception of that nerve, and 3) pain relieved by local anaesthetic.4
One of the other symptoms we may see in an area of nerve damage is a small outpouching in the area of decreased innervation on the front lower abdominal wall.
So, what can we do with this information? The good news is that as rehab professionals, we can treat along the fascial pathway of the nerve to release in key areas of entrapment. We can mobilize the nerve directly. Neural tension testing can help us differentiate the nerve in question and we can use neural glides and slides after having freed up the nerve from the area of compression. Then, we can increase the communication of the nerve with the muscles by using specific, localized strengthening and stretch in areas of prior compression. All of these techniques are taught in in our course, Lumbar Nerve Manual Treatment and Assessment. Come join us in San Diego May 3-5, 2019 to learn how to differentially diagnose and treat entrapment of all of the nerves of the lumbar plexus.
Okiemy, G., Ele, N., Odzebe, A. S., Chocolat, R., & Massengo, R. (2008). The ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerves. The anatomic bases in preventing postoperative neuropathies after appendectomy, inguinal herniorraphy, caesareans. Le Mali medical, 23(4), 1-4.
Whiteside, J. L., & Barber, M. D. (2005). Ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric neurectomy for management of intractable right lower quadrant pain after cesarean section: a case report. The Journal of reproductive medicine, 50(11), 857-859.
Turan, V., Colluoglu, C., Turkuilmaz, E., & Korucuoglu, U. (2011). Prevalence of diastasis recti abdominis in the population of young multiparous adults in Turkey. Ginekologia polska, 82(11).
Stulz, P., & Pfeiffer, K. M. (1982). Peripheral nerve injuries resulting from common surgical procedures in the lower portion of the abdomen. Archives of Surgery, 117(3), 324-327.

This post is a follow-up to the February 20th post written by Nancy Cullinane, "Pelvic Floor One is Heading to Kenya"
By the time folks are reading this, Nancy Cullinane, PT, MHS, WCS, Terri Lannigan, PT, DPT, OCS, and I will likely be in a warm, crowded classroom in Nairobi, Kenya helping 30+ “physios” navigate the world of misbehaving bladders, detailed anatomy description, and their first internal lab experiences. No doubt it will be both challenging and extremely rewarding. We are so grateful to the Herman & Wallace Pelvic Rehab Institute for sharing their curriculum in partnership with the Jackson Clinics Foundation to allow us to offer their valuable curriculum in order to affect positive health care changes.
I personally am humbled and honored to get to play a small but key role in the development of foundational knowledge and skills for these women PT’s who will no doubt change the lives of countless Kenyan women, and, consequently, their families.
My adventure truly began when I offered to write lectures on the topics of Fistula and FGM/C (female genital mutilation/cutting) and I began the process of crash course learning about these topics. The quest has taken me on a deep dive into professional journals, NGO websites, surgical procedure videos and insightful interviews with some of the pioneers working for years including “in the field” to help women in Africa and in countries where these issues are prevalent.
Before I began my research on the topic of fistula, I pretty much thought of a fistula as a hole between two structures in the body where it doesn’t belong, and narrowly thought of in terms of anal fistulas, acknowledging how lucky we are that there are skilled colorectal surgeons who can fix them. But after more research, my world view changed. (Operative word here being “world”).
A fistula is an abnormal or surgically made passage between a hollow or tubular organ and the body surface, or between two hollow or tubular organs. For our purposes here today, I am referring to an abnormal hole or passage between the vagina and the bladder, or rectum, or both. When the fistula forms, urine and/or stool passes through the vagina. The results are that the woman becomes incontinent and cannot control the leakage because the vagina is not designed to control these types of body fluids.
According to the Worldwide Fistula Fund, there are ~ 2 million women and girls suffering from fistulas. Estimates range from 30 to 100 thousand new cases developing each year; 3-5 cases/1000 pregnancies in low-income countries. A woman may suffer for 1-9 years before seeking treatment. For women who develop fistula in their first pregnancy, 70% end up with no living children.
Vesicovaginal fistulas (VVF) can involve the bladder, ureters, urethra, and a small or large portion of the vaginal wall. Women with VVF will complain of constant urine leakage throughout the day and night, and because the bladder never fills enough to trigger the urge to void, they may stop using the toilet altogether. During the exam there may be pooling of urine in the vagina.
Rectovaginal Fistula is less common, and accounts for ~ 10% of the cases. Women with RVF complain of fecal incontinence and may report presence of stool in the vagina. These women often will also have VVF.
In Kenya, most fistulas are obstetric fistulas, which occur as a result of prolonged obstetric labor (POL). These are also called gynecologic, genital, or pelvic fistulas. Traumatic fistulas account for 17-24 % of the cases and are caused by rape, sexual or other trauma, and sometimes even from FGM/C. The other type of fistula by cause is iatrogenic, meaning unintentionally caused by a health care provider during procedures such as during a C-section, hysterectomy, or other pelvic surgery. Most fistulas seen in the US are of this type.
Prolonged Obstructed Labor most often occurs when the infant’s head descends into the pelvis, but cannot pass though because of cephalo-pelvic disproportion (mismatch between fetus head and mother’s pelvis) thus creating sustained pressure on the tissues separating the tissues of the vagina and bladder or rectum, (or both) leading to a lack of blood flow and ultimately to necrosis of the tissue, and the development of the fistula. Those who develop this type of fistula spend an average of 3.8 days in labor (start of uterine contractions), some up to a week. In these cases, family members or traditional birth attendants may not recognize this is occurring, and even if they do, they may not have the instrumentation, the facilities or the skills necessary to handle the situation with an instrumental delivery or a C-section. And many of these women are in remote locations without transportation to appropriate facilities or lack the money to pay for procedures.
There are many adverse events and medical consequences that can result as a result of untreated obstetrical fistulas including the death of the baby in 90% of the cases. Physical effects besides the incontinence previously mentioned can include lower extremity nerve damage, which can be disabling for these women, along with a host of other physical and systemic health issues. The social isolation, ostracization by community, divorce, and loss of employment can lead to depression, premature lifespan, and sometimes suicide.
The good news is there are several great organizations making a difference.
In most cases, surgery is needed to repair the fistula. Sometimes, however, if the fistula is identified very early, it may be treated by placing a catheter into the bladder and allowing the tissues to heal and close on their own, and this is more viable in high-income countries after iatrogenic fistulas, but unfortunately, most women in the low-income countries have to wait for months or years before they receive any medical care.
There is an 80-90% cure rate depending on the severity, but according to the Worldwide Fistula Fund, 90% are left untreated, as the treatment capacity is only around 15,000 per year for the 100,00 new patients requiring it. Prevention is vital.
Despite successful repair of vesicovaginal fistulas, research shows that 15-35% of women report post-op incontinence at the time of discharge from the hospital, and that 45-100% of women may become incontinent in the years following their repair. Studies suggest that scar tissue-fibrosis of the abdominal wall and pelvis, and vaginal stenosis are strongly associated with post-operative incontinence.
According to research by Castille, Y-J et al in Int. J Gynecology Obstet 2014, there can be improved outcome of surgery both in terms of successful closure of vesicovaginal fistula and reduced risk of persistent urinary incontinence if women are taught a correct pelvic floor muscle contraction and advised to practice PFM exercise. Other studies have shown a positive effect from pre and post op PT in both post op urinary incontinence and PFM strength and endurance with a reduction of incontinence in more than 70% of treated patients, with improvements maintained at the 1year follow up. SO, THIS IS ONE REASON WE ARE SO EXCITED TO BE GOING TO KENYA!
I inquired about the use of dilators via email communication with surgeon Rachel Pope , MD MPH who has done extensive work in Malawi with women who have suffered from fistula, including the use of dilators, and her response was: “in women who have had obstetric fistula the dilators seem only marginally helpful after standard fistula repairs. The key is to have a good vaginal reconstructive surgery where skin flaps that still maintain their blood supply replace the area in the vagina previously covered by scar tissue. The dilators work exceedingly well when there is healthy tissue in place, and I think the overall outcomes are better for women in those scenarios compared to the cement-like scar we often see in women with fistulas.”
In the US, there are specialist surgeons who provide surgical repairs. While genitourinary fistulas can occur because of obstructed labor and operative deliveries in high income countries, they can also occur in a variety of pelvic surgeries, post pelvic radiation, as well as in cases of cancer, infections, with stones, and as well etiology includes instrumentations such as D&Cs, catheters, endoscopic trauma, and pessaries, and as well in cases of foreign bodies, accidental trauma, and for congenital reasons. As pelvic therapists it is important to know your patients’ surgical and medical history and to pay special attention to the patient’s history regarding their incontinence description and onset and be mindful during exam to notice possible pooling of urine in the vagina. Though rare in terms of occurrence, we should be aware of the possibility and may play a role in referring the patient to a physician who can do further diagnostic testing
In conclusion, I want to thank UK physiotherapist Gill Brook MCSP (DSA) CSP MSC, president of the IOPTWH who shared with me by interview her knowledge of fistula and experiences with the Addis Ababa Fistula Hospital in Ethiopia, which she has been visiting for 10 years, as well as Seattle’s Dr. Julie LaCombe MD FACOG who has performed fistula surgeries in Uganda and Bangladesh and met with me personally to share about obstetrical trauma and fistula surgery and management.
Nancy, Terri and I will look forward to sharing photos and more about our journey and experiences, upon our return. In the meantime, check out the Campaign to End Fistula and join the campaign.
Does cognitive self-regulation influence the pain experience by modulating representations of nociceptive stimuli in the brain or does it regulate reported pain via neural pathways distinct from the one that mediates nociceptive processing? Woo and colleagues devised an experiment to answer this question.1 They invited thirty-three healthy participants to undergo fMRI while receiving thermal stimulation trial runs that involved 6 levels of temperatures. Trial runs included “passive experience” where participants passively received and rated heat stimuli, and “regulation” runs, where participants were asked to cognitively increase or decrease pain intensity.
 Instructions for increasing pain intensity included statements such as “Try to focus on how unpleasant the pain is. Pay attention to the burning, stinging and shooting sensation.” Instructions for decreasing pain intensity included statements such as “Focus on the part of the sensation that is pleasantly warm. Imagine your skin is very cool and how good the stimulation feels as it warms you up.” The effects of both manipulations on two brain systems previously identified in the literature were examined. One brain system was the “neurological pain signature” (NPS), a distributed pattern of fMRI activity shown to specifically track pain intensity induced by noxious inputs. The second system was the pathway connecting the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) with the nucleus accumbens (NAc), shown to play a role in both reappraisal and modulation of pain. In humans, the vmPFC tracks spontaneous pain when it has become chronic and potentially dissociated from nociception.2,3 In patients with sub-acute back pain, the vmPFC-NAc connectivity has been shown to predict subsequent transition to chronic back pain.4 In addition, the vmPCF is hypothesized to play a role in the construction of self-representations, assigning personal value to self-related contents and, ultimately, influencing choices and decisions.5
Instructions for increasing pain intensity included statements such as “Try to focus on how unpleasant the pain is. Pay attention to the burning, stinging and shooting sensation.” Instructions for decreasing pain intensity included statements such as “Focus on the part of the sensation that is pleasantly warm. Imagine your skin is very cool and how good the stimulation feels as it warms you up.” The effects of both manipulations on two brain systems previously identified in the literature were examined. One brain system was the “neurological pain signature” (NPS), a distributed pattern of fMRI activity shown to specifically track pain intensity induced by noxious inputs. The second system was the pathway connecting the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) with the nucleus accumbens (NAc), shown to play a role in both reappraisal and modulation of pain. In humans, the vmPFC tracks spontaneous pain when it has become chronic and potentially dissociated from nociception.2,3 In patients with sub-acute back pain, the vmPFC-NAc connectivity has been shown to predict subsequent transition to chronic back pain.4 In addition, the vmPCF is hypothesized to play a role in the construction of self-representations, assigning personal value to self-related contents and, ultimately, influencing choices and decisions.5
Woo and colleagues found that both heat intensity and self-regulation strongly influenced reported pain, however they did so by two differing pathways. The NPS mediated only the effects of nociceptive input. The self-regulation effects on pain were mediated by the NAc-vmPFC pathway, which was unresponsive to the intensity of nociceptive input. The NAc-vmPFC pathway responded to both “increase” and “decrease” self-regulation conditions. Based on these results, study authors suggest that pain is influenced by both noxious input and cognitive self-regulation, however they are modulated by two distinct brain mechanisms. While the NPS encodes brain activity closely tied to primary nociceptive processing, the NAc-vmPFC pathway encodes information about evaluative aspects of pain in context. This research is limited in that the distinction between pain intensity and pain unpleasantness was not included and the subjects were otherwise healthy. Further research is warranted on the effects of this cognitive self-regulation model on brain pathways in patients with chronic pain conditions.
Even with the noted limitations, this research invites the clinician to consider the role of both nociceptive mechanisms and cognitive self-regulatory influences on a patient’s pain experience and suggests treatment choices should take both factors into consideration. Mindful awareness training is a treatment that contributes to cognitive self-regulatory brain mechanisms.6 When mindful, pain is observed as and labeled a sensation. The term “sensation” carries a neutral valence compared to “pain” which may reflect greater alarm or threat to an individual. The mind is recognized to have a camera lens-like quality that can shift from zoom to wide angle. While pain can draw attention in a more narrow focus on the painful body area, when mindful, an individual can deliberately adopt a wide angle view, focusing on pain free areas and other neutral or positive states. In addition, when mindful, the unpleasant sensation rests in awareness not characterized by fear and distress, but by stability, compassion and curiosity. Patients may not have control over the onset of pain, but with mindfulness training, they can take control over their response to the pain. This deliberate adoption of mindful principles and practices can contribute to cognitive self-regulatory brain mechanisms that can ultimately impact pain perception.
I am excited to share additional research and practical clinical strategies that help patients self-regulate their reactions to pain and other symptoms in my 2019 courses, Mindfulness for Rehabilitation Professionals at University Hospitals in Cleveland OH, April 6 and 7 and Mindfulness-Based Pain Treatment in Houston TX, October 26 and 27 and Portland OR May 18 and 19. Hope to see you there!
1. Woo CW, Roy M, Buhle JT, Wager TD. Distinct brain systems mediate the effects of nociceptive input and self-regulation on pain. PLoS;2015;13(1):e1002036.
2. Baliki MN, Chialvo DR, Geha PY, Levy RM, et al. Chronic pain and the emotional brain: specific brain activity associated with spontaneous fluctuations of intensity of chronic back pain.J Neurosci. 2006;26(47):12165-73.
3. Hashmi JA, Baliki MN, Huang L, et al. Shape shifting pain: chronification of back pain shifts brain representation from nociceptive to emotional circuits. Brain. 2013;136(pt9):2751-68.
4. Baliki MN, Peter B B, Torbey S, Herman KM, et al. Corticostriatal functional connectivity predicts transition to chronic back pain. Nat Neurosci.2012;15(8):1117-9.
5. D’Argembeau. On the role of the ventromedial prefrontal cortex in self-processing: The Valuation Hypothesis. Front Human Neurosci. 2013;7:372.
6. Zeidan F, Vago DR. Mindfulness meditation-based pain relief: a mechanistic account. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2016 Jun;1373(1):114-27.



















































